Construction
Noritake Itron VFDs have several methods of construction. The basic model is that of the frame type construction. The other variants are specific to the product type and are described in more detail in the relevant application notes associated with CIG (Chip in Glass Driver), Active Matrix and Rib Grid VFDs.
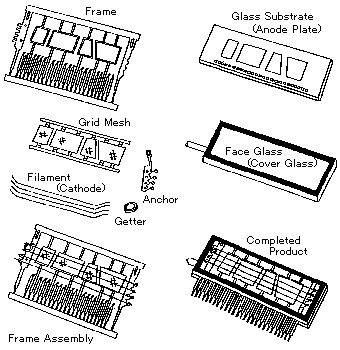
Fig.3 Frame Type Construction
The Grid Rim, Filament Support and Lead Pins are provided on a single metal frame. The ends of the Grid Rim are extended to the outside of the envelope, and are formed as lead pins for the Grids. The Anode leads are extended into the envelope to connect with the pads which are placed on the glass substrate. Both ends of the filament are welded to the Filament Support and Anchor with the appropriate tension. The Frame is assembled with the Face Glass and Glass Substrate (Anode Plate). The Lead Pins are tinned and formed into a suitable shape for PC Board assembly. FRAME-Types require press formed metal dies for construction. They offer good production yield and high reliability against various environmental conditions.
The illuminating anodes are coated with phosphor which emits light when hit by the electrons. Each anode forms a segment or dot, which collectively form individual characters. When an anode is supplied with a positive voltage, it will attract the electrons which have been accelerated through the grid. The segment emits light when these electrons impact on the phosphor coating. Alternatively when anodes are supplied with a negative voltage, they will repel electrons from their phosphor coating and therefore remain un-illuminated.
A hybrid of this construction mounts the grids directly on the glass substrate which allows complex grid patterns.
Guide to VFD Operation






