Basic Structure
Conventional CIG displays require a relatively large additional space for installing driver chips which causes the VFD size to be much larger. The Noritake Itron CIG VFD incorporates compact & high-density driver chips underneath the metal frame supporting the filament. For this reason, Noritake Itron CIG VFDs can be the same size as ordinary VFDs without driver chips. The absence of external driver chips allows for a substantial saving of space in the circuit design of the VFD and reduced assembly costs with improved MTBF capability.
Basic Structure
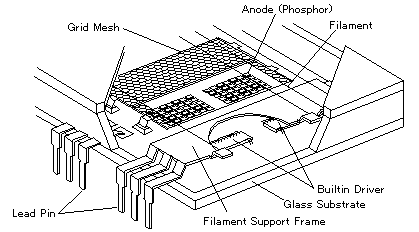
Fig.1 Basic Structure of CIG VFD
As can be seen in Fig. 1, the driver chip is located on the glass plate under the frame, and connected by wire bonding to the electrodes which are located on the glass plate. The data and power supplies to the drivers are connected to the lead pins through the conductive tracks on the plate. The output of the drivers go through the conductive tracks located on the same plate to reach their respective segments (phosphors) and/or grids.
CIG Driver Chip
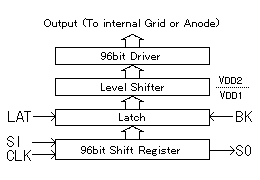
Fig.2 Logic Diagram of CIG Driver (96bit type)
The CIG VFD incorporates one to four 96-bit, 128-bit or 144bit drivers, depending on the display pattern demanded by the application. Like the driver ICs in ordinary VFDs, the drivers in CIG VFD contain level shifters, latches, and shift registers made of C-MOS FET circuits as shown in Fig. 2.
The devices are less than 10mm in length with very fine bonding pitches along one side which requires Noritake to employ the world's fastest fine pitch bonding machines.
Chip in Glass VFD (BD-VFD)
-
Operation and Structure
-
Power Supply
-
CIG VFD Interfacing
-
Control Procedure
-
Custom Design Guidance
-
Others






