CIG VFD Drive Methods
CIG VFD Drive Methods
The CIG VFDs can be classified into two types of drive method known as ' static' or ' multiplex' drive, and in multiplex drive there are two interconnection types known as Grid Anode hybrid interlacing or Grid Anode independent. Each type has different driving procedure.
Static Drive - Each anode driven by a dedicated driver output.
Hybrid Interlace - Anodes and grids combined on one serial driver.
Independent - Anodes and grids have separate serial drivers.
Static Drive
The static drive type requires each output from the driver to be directly connected to a corresponding segment. The grid voltage is supplied directly from the lead pins to a common grid covering all the anodes without passing through the driver circuits. Static drive has the disadvantage of using a greater number of driver outputs compared to multiplex drive.
It does however offer some important advantages, such as freedom of segment patterning and the dead space for grid division is not necessary. Also, the driving voltage can be 12V and higher brightness can easily be obtained.
Therefore, the static driven CIG VFD is suitable for applications which require flexible segment design, lower power consumption and/or higher brightness. Fig. 3 represents a logic diagram of the static driven CIG VFD with two 96 bit driver chips which can drive a maximum of 192 segments.
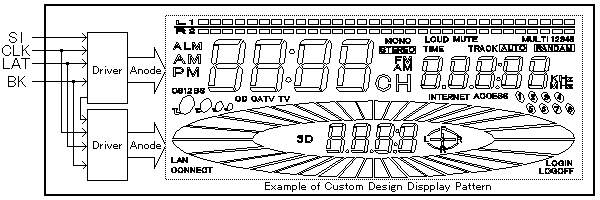
Fig.3 Example of Static Drive Type
Multiplex Drive
In a multiplex driven CIG VFD, the outputs from the built-in driver are also assigned to each grid. This type is further subdivided into two categories; a grid / anode hybrid interlace type in which the anode (segment) data and grid scan data are obtained from one driver (Fig. 4), and a grid / anode independent type which contains a dedicated grid driver and dedicated anode driver, separately (Fig. 5).
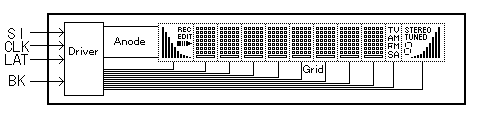
Fig.4 Example of Grid Anode Hybrid Interlace Type
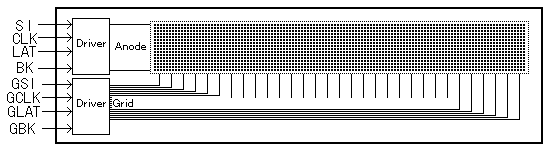
Fig.5 Example of Grid Anode Independent Type
The hybrid interlace type minimizes the number of drivers, which may allow cost reduction, and is especially suitable for displays were the number of segments is low. The control software for the hybrid interlace type may be more complex because the grid scan data and the anode data must be contained in the same serial data stream.
The independent type is able to control the grid data and the anode data separately. Therefore, it can provide a driving scheme more similar to a conventional VFD, and can be used for a relatively large number of display segments. In either case, the multiplex drive type can drive many segments with a small number of drivers. The resulting advantage is that the circuit space can be reduced, and the whole system cost is reduced, as compared to a display with external driver ICs.
Chip in Glass VFD (BD-VFD)
-
Operation and Structure
-
Power Supply
-
CIG VFD Interfacing
-
Control Procedure
-
Custom Design Guidance
-
Others






